
The multiplication of ground-breaking technologies has totally changed the way how the world hailed so far. With digitalism going at a reinforcing pace, IT infrastructure pioneers are put under a difficult situation.
IT Infrastructure Challenges – A Primer
The multiplication of ground-breaking technologies has totally changed the way how the world hailed so far. With digitalism going at a reinforcing pace, IT infrastructure pioneers are put under a difficult situation. Your traditional IT infrastructure cannot stand a chance to keep pace with the emerging technologies. The absence of transparency in the network infrastructure can cause an adverse effect on the business. These IT framework difficulties may prompt expanded expense of tasks; decline in profitability, decreased consumer loyalty, security dangers, surging maintenance costs and of all, at last it can cut down the brand picture.
IT infrastructure is an expansive field which contains different components such as network and security structure, storage and servers, business applications, operating systems, as well as databases. Some of the core components need cautious administration, which is often challenging for the organizations. Some of the major challenges that the companies face today are: data acquisition, data storage architectures, computing platforms, compute provisioning and management, data analytics, and networks and communication.
To fix the problem of interoperability and avoid fazing patch solutions, a distinct environment for new technologies has to be introduced. This is where cloud services come into the picture.
Transition to the Cloud
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a term used to describe both a platform and type of application. It alludes to both the applications delivered as services over the web and the hardware and frameworks in the data centers that provide those services. Cloud computing is a computing technique in which scalable and lithe IT functionalities are delivered as an overhaul to outside customers using Internet technologies. It is an evolutionary concept that integrates manifold existent technologies to offer a useful new IT provisioning tool and conveys IT as an administration.
It provides highly scalable distributed computing systems in which computational resources are offered ‘as a service’. It is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources such as networks, servers, storage, applications and services that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Resources are used as an aggregated digital laptop.
Basically a cloud is built over a number of the data centers, which reflects the Web’s context for loosely coupled systems (i.e. two systems don’t know about each other), and provides the ability to have virtualized remote servers through standard Web services to have large computing power. Cloud paradigm also serves as a business model apart from technology.
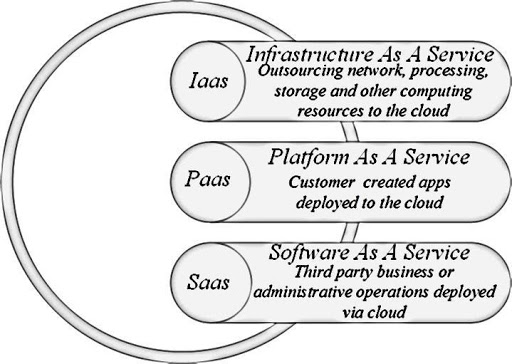
Cloud Computing is categorized into three distinct areas such as:
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) The consumer can use the provider’s applications running on the cloud. The cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud clients.
- PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service) The consumer can deploy, the consumer created or acquired applications created by using programming languages or tools provided by provider, on the cloud infrastructure. The cloud providers deliver a computing platform typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and execute their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers
- IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) The consumer can provision processing, storage, networks and other fundamental computing resources where the consumers can deploy and run the software (i.e. operating systems, applications. IaaS suppliers offer computers, as physical or more often as virtual machines, and different assets.
Deployment Models of Cloud
Clouds can also be classified based upon the underlying infrastructure deployment models as below:
- Public Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is available to the general public
- Private Cloud The type of the cloud, that is available solely for a single organization
- Hybrid Cloud This is a cloud infrastructure that is a composition of two or more clouds i.e. private, community or public
- Community Cloud the infrastructure of the cloud is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community with shared concerns
The different infrastructure deployment models are distinguished with their own characteristics. The characteristics to describe the deployment models are:
- Who owns the infrastructure
- Who manages the infrastructure
- Where is the infrastructure located
- Who has access to the cloud services
- Technical requirements such as Operability of different database frameworks, load balancing, licensing ramifications, bandwidth limitations
Cloud Computing Challenges
The decision to adopt Cloud Computing is challenging because of the range of practical and socio political reasons. It is unimaginable that all enterprises outsource their whole back end computing requirements to cloud providers rather; they will build up a heterogeneous computing environment which depends on dedicated servers, organizational clouds and possibly more than one public cloud provider.
How the adoption to Cloud Computing is managed does not only depend on technical issues but also on socio-technical factors (i.e. cost, confidentiality and control), the impact on work practices and constraints derived from existing business models.

Cloud Computing Benefits
- Cloud technology is paid incrementally, saving organizations money.
- Organizations can store more data than on private computer systems.
- No longer do IT personnel need to worry about keeping software up to date.
- Cloud computing offers much more flexibility than past computing methods.
- Employees can access information wherever they are, rather than having to remain at their desks.
- No longer having to worry about constant server updates and other computing issues, government organizations will be free to concentrate on innovation.
- Decoupling and separation of the business service from the infrastructure needed to run it (virtualization).
- Flexibility to choose multiple vendors that provide reliable and scalable business services, development environments, and infrastructure that can be leveraged out of the box and billed on a metered basis with no long term contracts.
- Elastic nature of the infrastructure to rapidly allocate and de-allocate massively scalable resources to business services on a demand basis.
- Cost allocation flexibility for customers wanting to move CapEx into OpEx. Cloud computing eliminates the capital costs of procuring hardware and software, configuring and operating local data centers, such as server racks, 24-hour power supply for power and cooling, and skilled IT professionals to manage this infrastructure.
- Reduced costs due to operational efficiencies and more rapid deployment of new business services. It enables users to get to the assets amongst users that help in centralization, peak-load capacity and great usage of available resources and better productivity.
Effective Ways of Managing the Infrastructure Resources
Infrastructure Management (IM) Services for Business – A Primer
Most IT businesses today will in general invest more energy responding to issues than attempting to remember them before they cause disturbance. For enterprises to run efficiently at optimal performance, infrastructure management services are essential. IT Infrastructure management is quickly becoming a solution that companies depend on in order to reduce the stress of maintaining and improving their IT resources.
For an organization’s information technology, infrastructure management (IM) is the management of essential operation components, such as policies, processes, equipment, data, human resources, and external contacts, for overall effectiveness.
Key components of IT InfrastructureThe key components of IT infrastructure are the hardware such as computers, servers, routers, switches and other equipment; software which includes productivity applications, enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM); networks which comprise Internet connection, Network enablement, firewall and security; and the human component that includes system administrators, network administrators, developers, etc.
Key services
IM should ensure that servers, networks and databases operate at peak efficiency, resolving system issues proactively, using automation and predictive analytical tools, deliver real-time business visibility and insights, ensures secure, compliant and predictable IT services – to accelerate the digital transformation journey for enterprises.
Infrastructure Management services include installation, consulting, continuous monitoring, updating, patching, servicing and managing of infrastructure at optimized cost. When we say infrastructure, they are data centers, storage farms, servers, networks and other layers of infrastructure that can be managed remotely with minimum human intervention.
Infrastructure management services can be broadly classified into systems management, network management and storage management
IT Infrastructure Management Challenges and solution
Powerful Computing
Processing of large amount of data with faster computing power is a major bottleneck. A simple solution to this challenge would be to utilize new broadly useful graphical processors or multi-core platforms.
Data Acquisition
Firewalls which secures emails, applications and web browsing can cause important packet losses in the TCP/IP networks. This can result in important data loss and reduce the network speeds considerably, making the online coordinated efforts impossible.
High-performance computing resources with huge data sets and a secure bridge to collaborate with dispersed scientific teams, sophisticated means to collect, filter and store high-speed networks is the solution.
Management and Provisioning
High-performance computing of these large data sets will require virtualization and automation to abstain from adding more people to these processes. The major challenge for IT managers is to streamline these errands and accelerate the preparing.
This challenge can be unraveled by using distributive frameworks. These frameworks separate complex assignments into littler free bits which can be handled by singular PCs which are associated with a network.
Data Storage Structures
Though cloud storage is a cost-effective and scalable alternative for IT managers, more flexibility is required in the cloud storage options.
It should be easy to optimize the cloud storage architecture according to the application which is being deployed. It needs to be more reliable, efficient and be able to handle a variety of applications and needs of the user community. The distributed storage alternatives need to fill in as long haul and recorded rather than a momentary answer for the IT people group.
Network and Connectivity
IT infrastructure management can be a difficult task for any IT manager of the organization without a reliable network connection. Data optimization is possible only with new software-based methods and system engineering structure.
The capacity to relocate the IP address would help to allow application services to be migrated to other hardware. Another solution to this challenge would be to add intelligence to the wired as well as Wi-Fi network connections. This will help the networks to optimize the traffic delivery to contain costs and improve the service.
Benefits of IM Services
Usage of the Best of Technology
IT services are constantly upgraded with zero additional cost or financial risk. Thus, businesses don’t have to worry about usage of antiquated technology
Improved Productivity
Recognizable proof of issue is important for improvement to be sought. Infrastructure services help the teams understand how the network functions and accordingly tweak the framework. These services proactively identify problematic areas. Detecting potential issues helps businesses in averting future downtime to end users.
Centralization of applications
A managed infrastructure service is more robust in dealing with the network infrastructure. With a managed IT services network, enterprises centralize all applications and servers within managed data centers. This leads to improved employee performance regardless of location. Access to unified data centers within the network can also provide admission to virtual services, as well as storage and backup infrastructure.
Reduce Infrastructure cost and operational activities
A managed IT infrastructure service offers the highest quality inventiveness and carrier-grade solutions to customers. A fixed monthly payment plan paves way for predictable monthly costs. This way, enterprises know how much it’s going to cost them and there are no unexpected upgrade charges
Conclusion
Cloud Computing is undoubtedly a growing revolution within IT. However, as with any paradigm shift, there are risks and rewards which need to be finely balanced. Cloud Computing carries exceptional advantages to organizations and will be the dominant way of acquiring technology in the future but IT decision makers are confused with the number of vendors available in the market place. a full due diligence process be undertaken when assessing vendors and that, where appropriate, independent advice should be obtained that matches the product offering with the business requirements.
About Author
Manoj Yadav is Chief Technical Evangelist for Prismberry. Manoj has more than 20+ years in the IT industry and has been part of successful teams who build cost-effective and scalable solutions to customers. At Prismberry Manoj is responsible for delivering cloud solutions to end customers across verticals. Manoj can be reached @ manoj@prismberry.com or through https://www.linkedin.com/in/manojyadavcso/

















